@roobal Dlaczego nic się nie zmienia przy użyciu chmod na katalog /media/Dodatkowy (mój drugi dysk)?
Teraz po zastosowaniu chmod -R 777 mam błąd że nie można zlalezć pliku, mimo że mogłem wprowadzić ścieżkę.
Źle, w libvirtd.conf odkomentowujesz user i group libvirt, dodajesz usera do grupy libvirt, restartujesz usługę libvirtd, przelogowujesz się i virt managerem stawiasz maszyny jako user, nie root.
Ntfs nie bierze pod uwagę linuksowych uprawnień, więc nie powinieneś miec access denied. Ja cześć maszyn mam na dysku z ntfs, część na dysku z ext4 i przy tych ustawieniach nie mam żadnych problemów z tworzeniem maszyn, vDysków itp. jako user.
@roobal
Wracam z tym tematem, mam nowy system (dalej LMDE2) i zacząłem wszystko od nowa. Mam użytkownika libvirt w grupie libvirt.
W virt-manager mam taki błąd:
[code] Nie można połączyć z biblioteką libvirt.
Proszę sprawdzić, czy demon “libvirtd” jest uruchomiony.
Libvirt URI is: qemu:///system
Traceback (most recent call last):
File “/usr/share/virt-manager/virtManager/connection.py”, line 1020, in _open_thread
self._backend.open(self._do_creds_password)
File “/usr/share/virt-manager/virtinst/connection.py”, line 158, in open
open_flags)
File “/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/libvirt.py”, line 105, in openAuth
if ret is None:raise libvirtError(‘virConnectOpenAuth() failed’)
libvirtError: Failed to connect socket to ‘/var/run/libvirt/libvirt-sock’: Połączenie odrzucone[/code]
Jak chce ją włączyć w terminalu to:
[code] service libvirtd start
[…] Starting libvirt management daemon: libvirtd/usr/sbin/libvirtd: error: Unable to obtain pidfile. Check /var/log/messages or run without --daemon for more info.
failed!
libvirtd
2017-05-05 12:06:40.779+0000: 4574: info : libvirt version: 1.2.9, package: 9+deb8u3 (buildd 2016-07-01-18:17:10 x86-grnet-01)
2017-05-05 12:06:40.779+0000: 4574: error : virPidFileConstructPath:554 : Cannot create user runtime directory ‘/run/user/1000/libvirt’: Brak dostępu
2017-05-05 12:06:40.780+0000: 4574: error : main:1286 : Can’t determine pid file path.
[/code]
Od komentowałem linijki w libvirtd.conf
[code] # Master libvirt daemon configuration file
For further information consult http://libvirt.org/format.html
NOTE: the tests/daemon-conf regression test script requires
that each “PARAMETER = VALUE” line in this file have the parameter
name just after a leading “#”.
#################################################################
Network connectivity controls
Flag listening for secure TLS connections on the public TCP/IP port.
NB, must pass the --listen flag to the libvirtd process for this to
have any effect.
It is necessary to setup a CA and issue server certificates before
using this capability.
This is enabled by default, uncomment this to disable it
#listen_tls = 0
Listen for unencrypted TCP connections on the public TCP/IP port.
NB, must pass the --listen flag to the libvirtd process for this to
have any effect.
Using the TCP socket requires SASL authentication by default. Only
SASL mechanisms which support data encryption are allowed. This is
DIGEST_MD5 and GSSAPI (Kerberos5)
This is disabled by default, uncomment this to enable it.
#listen_tcp = 1
Override the port for accepting secure TLS connections
This can be a port number, or service name
#tls_port = “16514”
Override the port for accepting insecure TCP connections
This can be a port number, or service name
#tcp_port = “16509”
Override the default configuration which binds to all network
interfaces. This can be a numeric IPv4/6 address, or hostname
If the libvirtd service is started in parallel with network
startup (e.g. with systemd), binding to addresses other than
the wildcards (0.0.0.0/: might not be available yet.
might not be available yet.
#listen_addr = “192.168.0.1”
Flag toggling mDNS advertizement of the libvirt service.
Alternatively can disable for all services on a host by
stopping the Avahi daemon
This is disabled by default, uncomment this to enable it
#mdns_adv = 1
Override the default mDNS advertizement name. This must be
unique on the immediate broadcast network.
The default is “Virtualization Host HOSTNAME”, where HOSTNAME
is substituted for the short hostname of the machine (without domain)
#mdns_name = “Virtualization Host Joe Demo”
#################################################################
UNIX socket access controls
Beware that if you are changing any of these options, and you use
socket activation with systemd, you need to adjust the settings in
the libvirtd.socket file as well since it could impose a security
risk if you rely on file permission checking only.
Set the UNIX domain socket group ownership. This can be used to
allow a ‘trusted’ set of users access to management capabilities
without becoming root.
This is restricted to ‘root’ by default.
unix_sock_group = “libvirt”
Set the UNIX socket permissions for the R/O socket. This is used
for monitoring VM status only
Default allows any user. If setting group ownership, you may want to
restrict this too.
unix_sock_ro_perms = “0777”
Set the UNIX socket permissions for the R/W socket. This is used
for full management of VMs
Default allows only root. If PolicyKit is enabled on the socket,
the default will change to allow everyone (eg, 0777)
If not using PolicyKit and setting group ownership for access
control, then you may want to relax this too.
unix_sock_rw_perms = “0770”
Set the name of the directory in which sockets will be found/created.
unix_sock_dir = “/var/run/libvirt”
#################################################################
Authentication.
- none: do not perform auth checks. If you can connect to the
socket you are allowed. This is suitable if there are
restrictions on connecting to the socket (eg, UNIX
socket permissions), or if there is a lower layer in
the network providing auth (eg, TLS/x509 certificates)
- sasl: use SASL infrastructure. The actual auth scheme is then
controlled from /etc/sasl2/libvirt.conf. For the TCP
socket only GSSAPI & DIGEST-MD5 mechanisms will be used.
For non-TCP or TLS sockets, any scheme is allowed.
- polkit: use PolicyKit to authenticate. This is only suitable
for use on the UNIX sockets. The default policy will
require a user to supply their own password to gain
full read/write access (aka sudo like), while anyone
is allowed read/only access.
Set an authentication scheme for UNIX read-only sockets
By default socket permissions allow anyone to connect
To restrict monitoring of domains you may wish to enable
an authentication mechanism here
#auth_unix_ro = “none”
Set an authentication scheme for UNIX read-write sockets
By default socket permissions only allow root. If PolicyKit
support was compiled into libvirt, the default will be to
use ‘polkit’ auth.
If the unix_sock_rw_perms are changed you may wish to enable
an authentication mechanism here
#auth_unix_rw = “none”
Change the authentication scheme for TCP sockets.
If you don’t enable SASL, then all TCP traffic is cleartext.
Don’t do this outside of a dev/test scenario. For real world
use, always enable SASL and use the GSSAPI or DIGEST-MD5
mechanism in /etc/sasl2/libvirt.conf
#auth_tcp = “sasl”
Change the authentication scheme for TLS sockets.
TLS sockets already have encryption provided by the TLS
layer, and limited authentication is done by certificates
It is possible to make use of any SASL authentication
mechanism as well, by using ‘sasl’ for this option
#auth_tls = “none”
Change the API access control scheme
By default an authenticated user is allowed access
to all APIs. Access drivers can place restrictions
on this. By default the ‘nop’ driver is enabled,
meaning no access control checks are done once a
client has authenticated with libvirtd
#access_drivers = [ “polkit” ]
#################################################################
TLS x509 certificate configuration
Override the default server key file path
#key_file = “/etc/pki/libvirt/private/serverkey.pem”
Override the default server certificate file path
#cert_file = “/etc/pki/libvirt/servercert.pem”
Override the default CA certificate path
#ca_file = “/etc/pki/CA/cacert.pem”
Specify a certificate revocation list.
Defaults to not using a CRL, uncomment to enable it
#crl_file = “/etc/pki/CA/crl.pem”
#################################################################
Authorization controls
Flag to disable verification of our own server certificates
When libvirtd starts it performs some sanity checks against
its own certificates.
Default is to always run sanity checks. Uncommenting this
will disable sanity checks which is not a good idea
#tls_no_sanity_certificate = 1
Flag to disable verification of client certificates
Client certificate verification is the primary authentication mechanism.
Any client which does not present a certificate signed by the CA
will be rejected.
Default is to always verify. Uncommenting this will disable
verification - make sure an IP whitelist is set
#tls_no_verify_certificate = 1
A whitelist of allowed x509 Distinguished Names
This list may contain wildcards such as
“C=GB,ST=London,L=London,O=Red Hat,CN=*”
See the POSIX fnmatch function for the format of the wildcards.
NB If this is an empty list, no client can connect, so comment out
entirely rather than using empty list to disable these checks
By default, no DN’s are checked
#tls_allowed_dn_list = [“DN1”, “DN2”]
A whitelist of allowed SASL usernames. The format for usernames
depends on the SASL authentication mechanism. Kerberos usernames
look like username@REALM
This list may contain wildcards such as
“*@EXAMPLE.COM”
See the POSIX fnmatch function for the format of the wildcards.
NB If this is an empty list, no client can connect, so comment out
entirely rather than using empty list to disable these checks
By default, no Username’s are checked
#sasl_allowed_username_list = [“joe@EXAMPLE.COM”, "fred@EXAMPLE.COM" ]
#################################################################
Processing controls
The maximum number of concurrent client connections to allow
over all sockets combined.
#max_clients = 5000
The maximum length of queue of connections waiting to be
accepted by the daemon. Note, that some protocols supporting
retransmission may obey this so that a later reattempt at
connection succeeds.
#max_queued_clients = 1000
The maximum length of queue of accepted but not yet not
authenticated clients. The default value is zero, meaning
the feature is disabled.
#max_anonymous_clients = 20
The minimum limit sets the number of workers to start up
initially. If the number of active clients exceeds this,
then more threads are spawned, up to max_workers limit.
Typically you’d want max_workers to equal maximum number
of clients allowed
#min_workers = 5
#max_workers = 20
The number of priority workers. If all workers from above
pool are stuck, some calls marked as high priority
(notably domainDestroy) can be executed in this pool.
#prio_workers = 5
Total global limit on concurrent RPC calls. Should be
at least as large as max_workers. Beyond this, RPC requests
will be read into memory and queued. This directly impacts
memory usage, currently each request requires 256 KB of
memory. So by default up to 5 MB of memory is used
XXX this isn’t actually enforced yet, only the per-client
limit is used so far
#max_requests = 20
Limit on concurrent requests from a single client
connection. To avoid one client monopolizing the server
this should be a small fraction of the global max_requests
and max_workers parameter
#max_client_requests = 5
#################################################################
Logging controls
Logging level: 4 errors, 3 warnings, 2 information, 1 debug
basically 1 will log everything possible
Note: Journald may employ rate limiting of the messages logged
and thus lock up the libvirt daemon. To use the debug level with
journald you have to specify it explicitly in ‘log_outputs’, otherwise
only information level messages will be logged.
#log_level = 3
Logging filters:
A filter allows to select a different logging level for a given category
of logs
The format for a filter is one of:
x:name
x:+name
where name is a string which is matched against source file name,
e.g., “remote”, “qemu”, or “util/json”, the optional “+” prefix
tells libvirt to log stack trace for each message matching name,
and x is the minimal level where matching messages should be logged:
1: DEBUG
2: INFO
3: WARNING
4: ERROR
Multiple filters can be defined in a single @filters, they just need to be
separated by spaces.
e.g. to only get warning or errors from the remote layer and only errors
from the event layer:
#log_filters=“3:remote 4:event”
Logging outputs:
An output is one of the places to save logging information
The format for an output can be:
x:stderr
output goes to stderr
x:syslog:name
use syslog for the output and use the given name as the ident
x:file:file_path
output to a file, with the given filepath
x:journald
output to journald logging system
In all case the x prefix is the minimal level, acting as a filter
1: DEBUG
2: INFO
3: WARNING
4: ERROR
Multiple outputs can be defined, they just need to be separated by spaces.
e.g. to log all warnings and errors to syslog under the libvirtd ident:
#log_outputs=“3:syslog:libvirtd”
Log debug buffer size:
This configuration option is no longer used, since the global
log buffer functionality has been removed. Please configure
suitable log_outputs/log_filters settings to obtain logs.
#log_buffer_size = 64
##################################################################
Auditing
This setting allows usage of the auditing subsystem to be altered:
audit_level == 0 -> disable all auditing
audit_level == 1 -> enable auditing, only if enabled on host (default)
audit_level == 2 -> enable auditing, and exit if disabled on host
#audit_level = 2
If set to 1, then audit messages will also be sent
via libvirt logging infrastructure. Defaults to 0
#audit_logging = 1
###################################################################
UUID of the host:
Provide the UUID of the host here in case the command
‘dmidecode -s system-uuid’ does not provide a valid uuid. In case
‘dmidecode’ does not provide a valid UUID and none is provided here, a
temporary UUID will be generated.
Keep the format of the example UUID below. UUID must not have all digits
be the same.
NB This default all-zeros UUID will not work. Replace
it with the output of the ‘uuidgen’ command and then
uncomment this entry
#host_uuid = “00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000”
###################################################################
Keepalive protocol:
This allows libvirtd to detect broken client connections or even
dead clients. A keepalive message is sent to a client after
keepalive_interval seconds of inactivity to check if the client is
still responding; keepalive_count is a maximum number of keepalive
messages that are allowed to be sent to the client without getting
any response before the connection is considered broken. In other
words, the connection is automatically closed approximately after
keepalive_interval * (keepalive_count + 1) seconds since the last
message received from the client. If keepalive_interval is set to
-1, libvirtd will never send keepalive requests; however clients
can still send them and the daemon will send responses. When
keepalive_count is set to 0, connections will be automatically
closed after keepalive_interval seconds of inactivity without
sending any keepalive messages.
#keepalive_interval = 5
#keepalive_count = 5
If set to 1, libvirtd will refuse to talk to clients that do not
support keepalive protocol. Defaults to 0.
#keepalive_required = 1 [/code]
Dodatkowo musiałem stworzyć ten katalog którego dotyczy błąd ponieważ go nie było.
Możesz mi krok po kroku pomóc to skonfigurować?
Mały offtop, przy wylogowywaniu sie z użytkownika libvirt cinamon wisi na tepecie z zegarem i nic nie da się zrobić, prócz przełączenia na osobny terminal z którego mogę zrobić restart. Jak to naprawić?
Poradziłem sobie z libvirt w prostacki sposób, mianowicie odinstalowałem wszystko i wyrzuciłem configi. Zasadniczo prawie maszynę już da się stworzyć ale jest 2 ale…
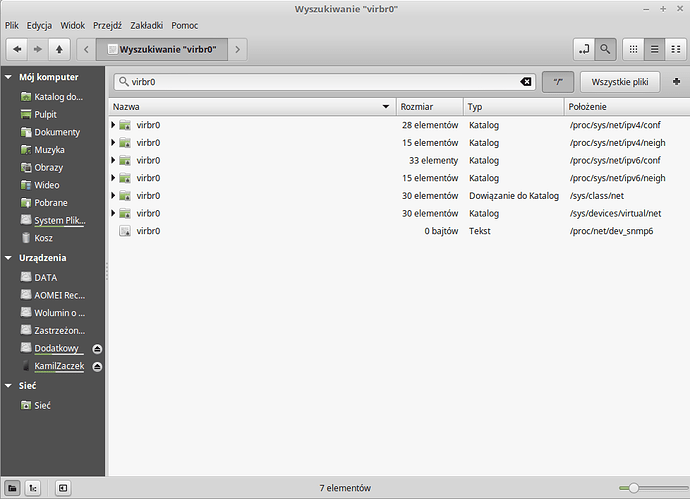
- Nie da się stworzyć interfejsu wirtualnego, jakiegokolwiek a błąd jest następujący:
[code] Błąd podczas tworzenia sieci wirtualnej: Unable to create bridge virbr0: File exists
Błąd podczas tworzenia sieci wirtualnej: Unable to create bridge virbr0: File exists
Traceback (most recent call last):
File “/usr/share/virt-manager/virtManager/asyncjob.py”, line 91, in cb_wrapper
callback(asyncjob, *args, **kwargs)
File “/usr/share/virt-manager/virtManager/createnet.py”, line 746, in _async_net_create
net.install()
File “/usr/share/virt-manager/virtinst/network.py”, line 199, in install
net.create()
File “/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/libvirt.py”, line 2820, in create
if ret == -1: raise libvirtError (‘virNetworkCreate() failed’, net=self)
libvirtError: Unable to create bridge virbr0: File exists
[/code]
I fakt istnieje sporo katalogów i plik z tą nazwą
Nie wiem czy mogę to usunąć.
- libvirt twierdzi że nia ma dostępu do dysku NTFS na którym sam stworzył obraz.
…
[code]Błąd podczas uruchamiania domeny: internal error: process exited while connecting to monitor: 2017-05-05T15:45:11.277048Z qemu-system-x86_64: -drive file=/media/zaku/Dodatkowy/VirtualMachines/HyperVWin/stor1.img,if=none,id=drive-sata0-0-1,format=raw: could not open disk image /media/kamil/Dodatkowy/VirtualMachines/HyperVWin/stor1.img: Could not open ‘/media/zaku/Dodatkowy/VirtualMachines/HyperVWin/stor1.img’: Permission denied
Błąd podczas uruchamiania domeny: internal error: process exited while connecting to monitor: 2017-05-05T15:45:11.277048Z qemu-system-x86_64: -drive file=/media/zaku/Dodatkowy/VirtualMachines/HyperVWin/stor1.img,if=none,id=drive-sata0-0-1,format=raw: could not open disk image /media/zaku/Dodatkowy/VirtualMachines/HyperVWin/stor1.img: Could not open ‘/media/zaku/Dodatkowy/VirtualMachines/HyperVWin/stor1.img’: Permission denied
Traceback (most recent call last):
File “/usr/share/virt-manager/virtManager/asyncjob.py”, line 91, in cb_wrapper
callback(asyncjob, *args, **kwargs)
File “/usr/share/virt-manager/virtManager/asyncjob.py”, line 127, in tmpcb
callback(*args, **kwargs)
File “/usr/share/virt-manager/virtManager/domain.py”, line 1355, in startup
self._backend.create()
File “/usr/lib/python2.7/dist-packages/libvirt.py”, line 999, in create
if ret == -1: raise libvirtError (‘virDomainCreate() failed’, dom=self)
libvirtError: internal error: process exited while connecting to monitor: 2017-05-05T15:45:11.277048Z qemu-system-x86_64: -drive file=/media/zaku/Dodatkowy/VirtualMachines/HyperVWin/stor1.img,if=none,id=drive-sata0-0-1,format=raw: could not open disk image /media/zaku/Dodatkowy/VirtualMachines/HyperVWin/stor1.img: Could not open ‘/media/zaku/Dodatkowy/VirtualMachines/HyperVWin/stor1.img’: Permission denied
[/code]
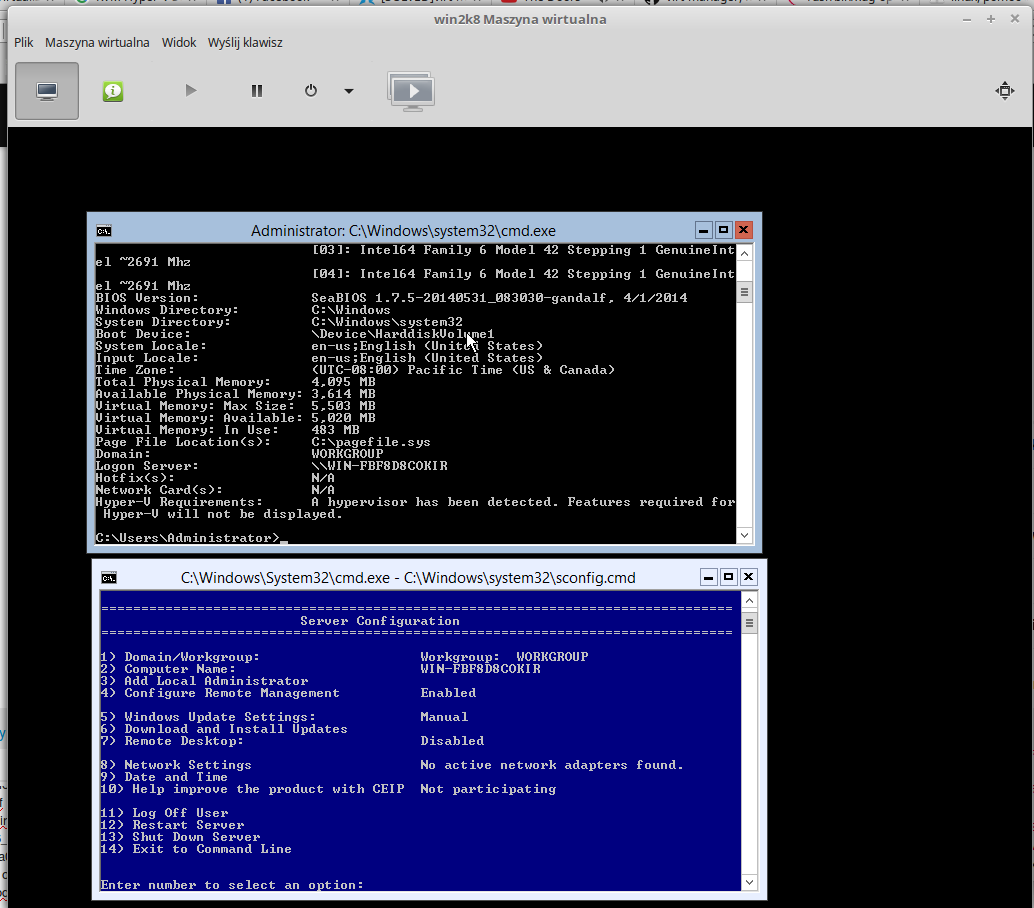
Zakładam też że przez brak odpowiednio dużego dysku (tylko 10GB na partycji linuxa, gdyż nie mam więcej miejsca) oraz brak interfejsu sieciowego w dalszym ciągu mam niedostępne usługi HyperV
Nie wiem jaki init ma lmde. Jeśli SysVinit, to używasz polecenia service. Jeśli systemd, systemctl. Jeśli chodzi o sieć, to musisz wywalić network manager (wyłączyć usługę). Następnie konfigurujesz sieć, tak jak bez GUI. Doinstalowujesz bridge-utils i tworzysz bridge, który następnie podpinasz do VMek.